In 2025, agents can handle 90% of your workflow, freeing you and your team to focus on what truly matters.
Today, we’re diving into CoAgents (CopilotKit), the full-stack framework for building user interactive agents and copilots.
We’ll explore integrations with leading agentic frameworks like LangGraph and CrewAI, discuss workflow automation, and highlight common pitfalls and best practices for avoiding them.
You’ll also get real-world automation examples with source code to help you implement these strategies.
Let’s jump in.
What is covered?
In a nutshell, we are covering these topics in detail.
- What are CoAgents with core components?
- Integration with CrewAI (Crews + Flows).
- What workflow automation means and common misconceptions.
- Some real-world examples with source code.
- Common pitfalls and best practices involved.
Note: Copilotkit (the framework for building AI Copilots) recently launched CoAgents with the partnership of LangChain and CrewAI. That is what we will be discussing in this.
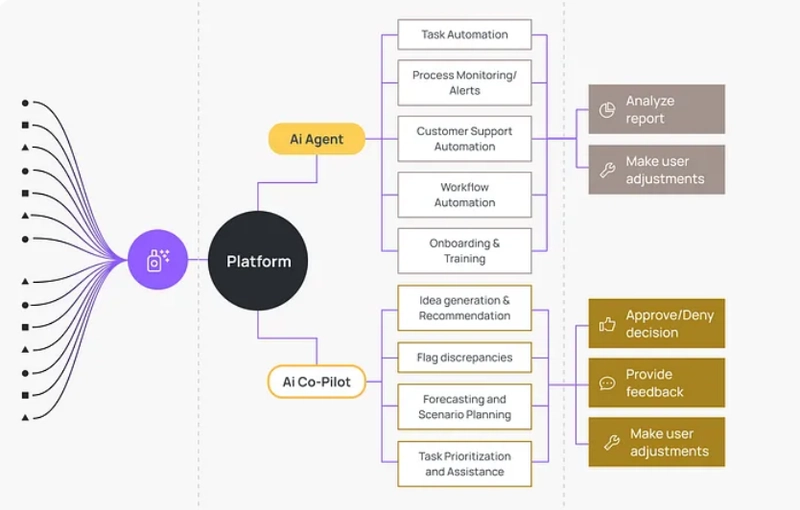
1. What are Agents?
AI agents are like really smart assistants. You just tell them what you need and they figure out how to get it done!!
The LLM acts as the brain of the system. When an AI has to communicate with the outside world, obtain data, or carry out particular tasks, it can utilize tools, which are external resources or APIs.
What are CoAgents?
It’s like this: Copilot + Agents = CoAgents(CopilotKit), used to break down tasks into smaller steps, coordinate actions, and work alongside humans (Human-in-the-loop).
For example, imagine Dan who is a sales professional, submits a travel reimbursement in the wrong currency which causes a major error. The automated workflow didn’t allow anyone else in the process to correct this mistake easily. CoAgents can step in, ask for human input at the right moment and correct things before they become bigger problems.
The framework to help you build it.
CopilotKit is a framework for integrating AI copilots into products. It offers React components for AI chat, generative UI, and autocomplete, plus a runtime that improves AI agents with context, tools and skills based on user behavior.
Developers can build CoAgents for any vertical by using LangGraph SDK + CoAgents (Copilotkit). Just build a LangGraph agent attuned to your workflow, then use CoAgents to integrate custom actions and generative UI experiences.

You can follow Agents 101: How to build your first agent in 30 minutes, a step-by-step guide to help you build CoAgents.
Check out CopilotKit’s GitHub ⭐️
Core Components.
This is done within a clean framework to manage CoAgents inside your application (thanks to LangGraph).
Let’s understand the core components:
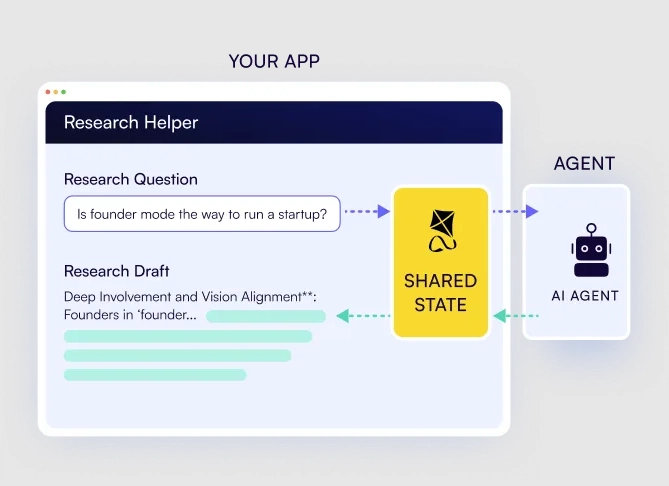
Shared State (Agent ↔ Application)– a synchronized state between the AI agent and the application, to make sure both have real-time access to the same information. This allows the agent to understand the application’s context and the application to monitor the agent’s actions.
const {state, setState} = useCoAgent("the agent name")
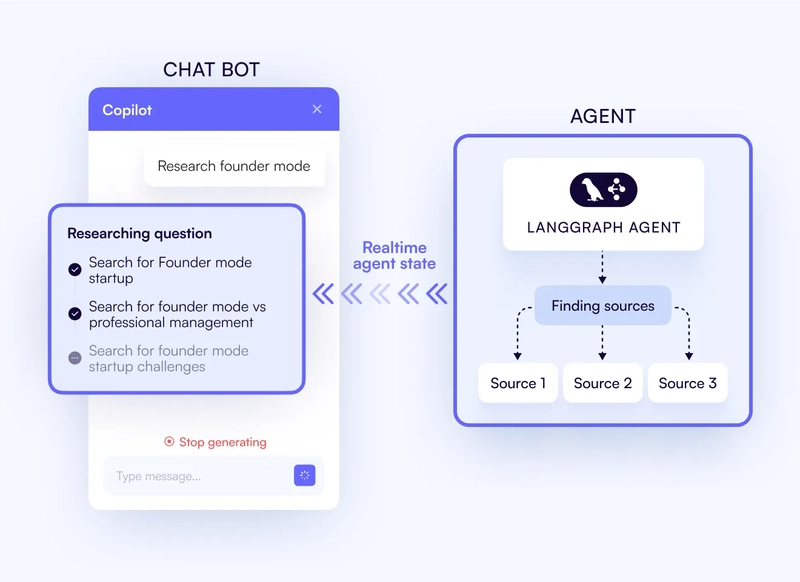
Agentic Generative UI– render the agent’s real-time state in the chat UI so the user can see what the agent is doing.
useCoagentStateRender(
name: "research_agent",
node: "download_progress",
render: ({ state, nodeName, status }) => {
return Progress logs={state.logs} /;
});
Human-in-the-Loop– specify breakpoints in the agent process at which Human input or approval is required. This ensures greater safety as well as better agent performance.
useCopilotAction({
name: "ApprovePlan",
parameters: [
{ name: "planSteps", type: "string[]" }
],
renderAndWait: ({ args, handler }) => (
<ConfirmPlan
planSteps={args.planSteps}
onApprove={(approvedSteps) => handler({ ... })}
onDeny={() => handler({ ... })}
/>
);

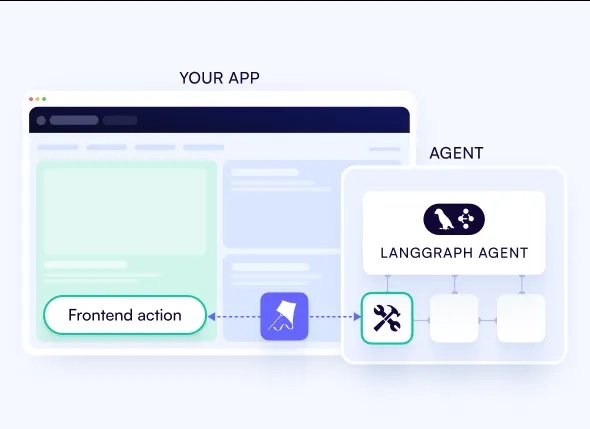
Realtime frontend actions– send frontend actions to the LangGraph agent as they become available. This allows the agent to explicitly take action within the application’s frontend in real-time, such as filling out forms.
useCopilotAction({
name: "InsertItemInList",
parameters: [
{ name: "city", type: "string" },
{ name: "country", type: "string" }
],
handler: ({ args, status }) => {
// ...
}
});
As per the docs, the future versions will include agent steering, enabling end-users to realign errant agents and subgraph support, among others.
You can read more on copilotkit.ai/coagents which also has illustrative diagrams to help you understand.


